Match the age group with the recommended therapeutic consideration – Matching Age Groups with Recommended Therapeutic Considerations sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate relationship between age and therapeutic approaches, providing healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools necessary to tailor treatments to the unique needs of each patient.
As we delve into the complexities of age-specific therapeutic considerations, we will uncover the impact of developmental characteristics on treatment efficacy, explore a comprehensive list of therapeutic options, and delve into the ethical implications of matching age groups with specific interventions.
Through engaging case studies and a forward-looking exploration of future directions, this guide empowers healthcare professionals to deliver age-appropriate, evidence-based care that optimizes patient outcomes.
Age Group Considerations: Match The Age Group With The Recommended Therapeutic Consideration
When matching age groups with therapeutic considerations, it is important to understand the developmental characteristics of different age groups. These characteristics can impact the effectiveness of therapeutic approaches.
Infants (0-12 months)
- Rapid physical and cognitive development
- Dependent on caregivers for physical and emotional needs
- Limited language and communication skills
Toddlers (1-3 years)
- Increased independence and mobility
- Developing language and communication skills
- Emergence of self-awareness and autonomy
Preschoolers (3-5 years)
- Increased social interaction and play
- Developing cognitive skills and problem-solving abilities
- Growing independence and self-regulation
School-aged Children (6-12 years)
- Formal education and increased academic demands
- Developing social and emotional skills
- Increased independence and self-reliance
Adolescents (13-18 years)
- Physical and hormonal changes
- Increased cognitive development and abstract thinking
- Developing identity and independence
Young Adults (19-25 years)
- Transition to adulthood and increased independence
- Continued cognitive and emotional development
- Exploration of identity and purpose
Adults (26-64 years)
- Physical and cognitive changes associated with aging
- Increased responsibilities and life experiences
- Developing coping mechanisms and resilience
Older Adults (65+ years)
- Increased physical and cognitive challenges
- Retirement and changes in social roles
- Increased need for support and healthcare
Therapeutic Considerations
When matching age groups with therapeutic considerations, it is important to consider a comprehensive list of therapeutic factors. These factors can include:
Treatment Goals
- The specific outcomes that the therapy aims to achieve
- Should be tailored to the individual needs of the client
- May change over time as the client progresses
Treatment Modality
- The specific type of therapy that is used
- Can include individual therapy, group therapy, or family therapy
- Should be selected based on the client’s needs and preferences
Treatment Setting, Match the age group with the recommended therapeutic consideration
- The location where the therapy takes place
- Can include a therapist’s office, a hospital, or a community center
- Should be chosen based on the client’s comfort and safety
Treatment Duration
- The length of time that the therapy will last
- Can vary depending on the client’s needs and the severity of the problem
- Should be determined in collaboration with the client
Treatment Frequency
- The number of times per week or month that the therapy will be provided
- Should be based on the client’s schedule and needs
- May change over time as the client progresses
Treatment Intensity
- The level of effort and engagement that is required from the client
- Should be tailored to the client’s capabilities and willingness
- May change over time as the client progresses
Matching Considerations
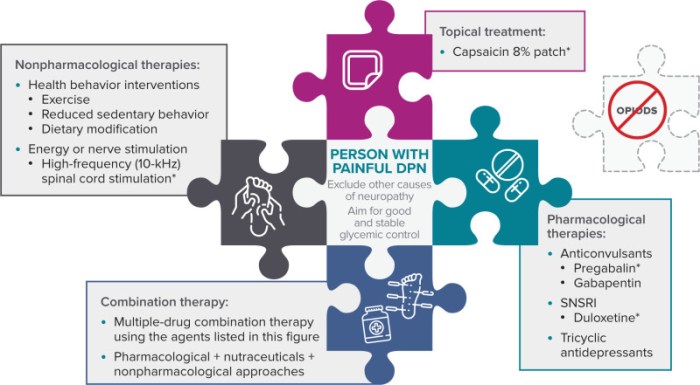
The process of matching age groups with therapeutic considerations involves carefully considering the developmental characteristics of the client and the therapeutic factors that are most appropriate for their needs. This process can be guided by the following steps:
1. Assess the Client’s Needs
- Determine the client’s age, developmental stage, and presenting problems
- Consider the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and support system
- Identify the specific therapeutic goals that need to be addressed
2. Review the Therapeutic Considerations
- Consider the different treatment modalities, settings, durations, frequencies, and intensities that are available
- Evaluate the pros and cons of each option
- Select the therapeutic factors that are most likely to meet the client’s needs
3. Make the Match
- Combine the client’s needs with the therapeutic considerations
- Develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the client’s individual needs
- Monitor the client’s progress and make adjustments as needed
Case Studies
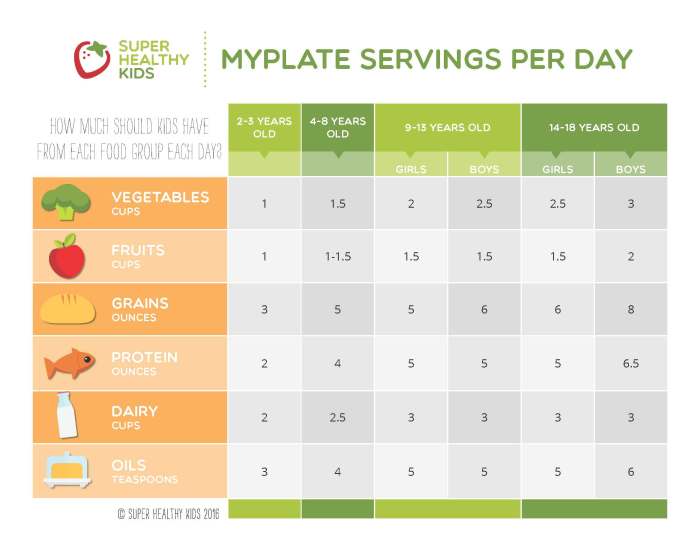
The following case studies demonstrate the application of matching age groups with therapeutic considerations:
Case Study 1
A 6-year-old boy with ADHD is struggling in school. He is easily distracted, has difficulty following instructions, and is often disruptive. The therapist matches the boy with a cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) program that is designed to improve his attention and self-regulation skills.
The therapy is provided in a group setting, twice a week for 12 weeks.
Case Study 2
A 15-year-old girl is experiencing depression and anxiety. She is withdrawn, has difficulty sleeping, and has lost interest in her usual activities. The therapist matches the girl with a psychodynamic therapy program that is designed to help her explore her underlying conflicts and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
The therapy is provided in an individual setting, once a week for 18 months.
Ethical Considerations
When matching age groups with therapeutic considerations, it is important to consider the ethical implications of the treatment. These implications include:
Informed Consent
- Clients should be fully informed about the nature of the therapy, the potential risks and benefits, and their right to refuse treatment
- For children and adolescents, informed consent should be obtained from both the client and their parents or guardians
Confidentiality
- Clients have a right to privacy and confidentiality
- Therapists should only disclose information about clients with their consent
- Exceptions to confidentiality may include situations where there is a risk of harm to the client or others
Competence
- Therapists should only provide services that they are qualified to provide
- Therapists should stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices
- Therapists should consult with other professionals when necessary
Future Directions
The field of matching age groups with therapeutic considerations is constantly evolving. Future directions for research and practice include:
Developing New Treatment Modalities
- Exploring new and innovative ways to deliver therapy
- Using technology to enhance the therapeutic experience
- Developing therapies that are tailored to specific age groups and populations
Improving Treatment Outcomes
- Conducting research to identify the most effective therapeutic approaches for different age groups
- Developing strategies to improve client engagement and retention
- Monitoring client progress and making adjustments as needed
Increasing Access to Therapy
- Reducing the stigma associated with mental health treatment
- Making therapy more affordable and accessible to all
- Training more therapists to work with children and adolescents
Q&A
What are the key factors to consider when matching age groups with therapeutic interventions?
Key factors include developmental characteristics, cognitive abilities, physical limitations, and potential side effects.
How can healthcare professionals ensure ethical decision-making in age-specific therapeutic considerations?
Healthcare professionals should prioritize patient autonomy, beneficence, and non-maleficence, and engage in shared decision-making with patients and their families.
What are the future directions for research and practice in matching age groups with therapeutic considerations?
Future directions include personalized medicine, precision therapeutics, and innovative technologies to enhance treatment efficacy and minimize age-related disparities in healthcare.